Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakayoshi, Akira; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Sasaki, Shinji; Maeda, Koji
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-011, 279 Pages, 2022/03
At the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), an investigation inside the reactors has been carried out, and R&D has been made on methods of fuel debris retrieval and storage after retrieval. In order to carry out the decommissioning work safely and steadily, understanding characteristics of fuel debris in the reactors is required. Therefore, in the development of technologies for grasping and analyzing properties of fuel debris project, the characteristics of simulated fuel debris, such as hardness, drying behavior, etc., of fuel debris for design of removal and storage, have been investigated and estimated, and provided to other projects conducting the decommissioning work. As part of this project, U-containing particles in samples (e.g., deposit on the investigation equipment, sediment in the reactors, etc.) obtained during the internal investigation of the reactors of 1F units 1 to 3 were analyzed. This report summarized the results of FE-SEM/WDX, FE-SEM/EDS, STEM/EDS, and TEM analysis, which were extracted from all analysis results obtained, as a database for the evaluation of the generation mechanism of U-containing particles. The analyses were performed at the JAEA Oarai Research and Development Institute and Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co., LTD.
Hidaka, Akihide
Fission Product Behavior under Severe Accident, p.85 - 88, 2021/05
no abstracts in English
Ando, Masaki
Hokeikyo Nyusu, (63), p.2 - 5, 2019/04
This is a commentary on the measurement of air dose rates by walk survey using KURAMA-II within 80 km range from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant, which has been conducted as a commissioned research from the Nuclear Regulation Authority. The outline of KURAMA-II, the distribution map of air dose rates obtained by walk surveys, and the result of analysis concerning the decreasing trend of air dose rates are introduced based on the previous reports and thesis.
Sasaki, Satoru
Gijutsushi, 29(3), p.4 - 7, 2017/03
Current status and issues of Fukushima prefecture after the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident were described both of the health effects of radiation exposure and the social effects. Important activities for revitalization in Fukushima are tackling of social task in Fukushima and understanding of correct radiation risk outside Fukushima. The role of the nuclear and radiation professional engineers for this activity was considered.
Sawaguchi, Takuma; Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo; Tanaka, Tadao
Hoken Butsuri, 50(1), p.36 - 49, 2015/03
It is desirable that the disaster wastes contaminated by radioactive cesium after the severe accident at the Fukushima Nuclear Plant are reused as much as possible in order to minimize the quantity to be disposed of. Ministry of the Environment showed the policy that the wastes containing cesium of higher concentration than the clearance level (100 Bq/kg) were reusable as materials of construction such as subbase course materials of pavements under controlled condition with measures to lower exposure doses. In this study, in order to provide technical information for making a guideline on the use of contaminated concrete materials recycled from disaster wastes as pavement, doses for workers and the public were estimated, and the reusable concentration of radioactive cesium in the wastes was evaluated. It was shown that the external exposure of the public (children) residing near the completed pavement gave the minimum radiocesium concentration in order to comply with the dose criteria. The recycled concrete materials whose average concentration of cesium lower than 2,700 Bq/kg can be used as the subbase course materials of pavements.
Nagai, Haruyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Esumi, Ayako
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hagiwara, Hiroki; Imoto, Jumpei; Hidaka, Akihide
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Putra, D.*; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Tomihara, Seiichi*; Watanabe, Shun*; Nagao, Seiya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Cs derived from Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant using the short-term emergency assessment system of marine environmental radioactivity
Cs derived from Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant using the short-term emergency assessment system of marine environmental radioactivityIkenoue, Tsubasa; Kawamura, Hideyuki; Kamidaira, Yuki
no journal, ,
In this study, we analyzed the characteristics and trends of oceanic dispersal of  Cs by performing the oceanic dispersion simulations using past oceanographic data received on the Short-Term Emergency Assessment system of Marine Environmental Radioactivity (STEAMER) developed at JAEA. Oceanic dispersion simulations in 1461 cases were carried out in the northwestern Pacific Ocean for 60 days from every day between 2015 and 2018. It was assumed that
Cs by performing the oceanic dispersion simulations using past oceanographic data received on the Short-Term Emergency Assessment system of Marine Environmental Radioactivity (STEAMER) developed at JAEA. Oceanic dispersion simulations in 1461 cases were carried out in the northwestern Pacific Ocean for 60 days from every day between 2015 and 2018. It was assumed that  Cs was released into the ocean from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant. In all calculation cases, the maximum concentration in 30 days at each computational grid (maximum concentration distribution) was calculated.
Cs was released into the ocean from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant. In all calculation cases, the maximum concentration in 30 days at each computational grid (maximum concentration distribution) was calculated.  Cs in the ocean surface in winter tended to be not dispersed so much. In the ocean surface, the seasonal variation was greater than the annual variation though the maximum concentration distributions have little annual variation. The average of the maximum concentration distribution in all calculation cases was inclined to be high from the coast of Fukushima to the offshore (140
Cs in the ocean surface in winter tended to be not dispersed so much. In the ocean surface, the seasonal variation was greater than the annual variation though the maximum concentration distributions have little annual variation. The average of the maximum concentration distribution in all calculation cases was inclined to be high from the coast of Fukushima to the offshore (140 E-145
E-145 E) and near the Kuroshio Extension.
E) and near the Kuroshio Extension.
Niizato, Tadafumi; Sasaki, Yoshito; Ito, Satomi; Watanabe, Takayoshi; Amamiya, Hiroki*
no journal, ,
An understanding of long-term environmental dynamics of radiocesium in forested area, which is released by the TEPCO's Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, is a key issue for predicting the future forest products radioactivity. In this paper we present the radiocesium uptake from forest floor in an evergreen Japanese cedar and a deciduous Japanese konara oak forests of the Abukuma Mountains, Fukushima. An investigation was conducted from 2015 to 2019. According to the International Biological Programme, IBP, annual radiocesium uptake from forest floor to the stand is estimated as follows; annual radiocesium increment associated with tree growth plus annual loss through litterfall, stemflow, and throughfall. The rate of annual radiocesium uptake to the total inventory of the stands associated with tree growth were estimated to be 0.1 and 0.06% in Japanese konara oak and Japanese cedar stands, respectively. The sum of radiocesium uptake including the loss of radiocesium amount by litterfall, stemflow, and throughfall were 1.37 and 3.13% in the konara oak and the cedar stands, respectively. The rate of radiocesium uptake estimated are lower than the elemental uptake in deciduous tree stands near Kyoto by IBP. This indicate that the radiocesium uptake by the konara oak and the cedar stands is limited and no significant increase in radiocesium concentration of tree tissues is expected in the study stands.
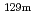 Te source term prediction at the beginning of Fukushima accident calculated reversely from the soil contamination map and atmospheric dispersion calculation, and recommendations for iodine and Cs source terms
Te source term prediction at the beginning of Fukushima accident calculated reversely from the soil contamination map and atmospheric dispersion calculation, and recommendations for iodine and Cs source termsHidaka, Akihide; Kawashima, Shigeto*; Kajino, Mizuo*; Takahashi, Sentaro*; Takahashi, Tomoyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English